Managing Scale Pests
Scale insect pests, order Homoptera, are usually of two types, the armored, family Diaspididae, or the soft, family Coccidae. Armored scale have a platelike shell and do not excrete honeydew whereas the honeydew excreted from soft scale insects often develop black sooty mold on plants. Small numbers can be tolerated, but infestations can explode depending on weather, naturally occurring predators and parasites, and the presence of honeydew-seeking ants that can gradually cause plant dieback or kill young plants.
Cultural / IPM Strategies : Scale pests increase as plant nitrogen levels increase; consider using slow-release fertilizer. Prevent access by ants (above all else) and take measures to keep the dust down. Scale shells can be rubbed off and pruning helps. Temperatures between 70 and 85 degrees and moderate to high humidity normally favor plant health and biological control. Insecticidal soap and oils are effective in the crawler stage. Any other chemicals, including fungicides, will interfere with or prevent effective biological control. Wait at least a month after using any residual pesticides. Breakdown of even lower risk pyrethrins takes longer in interiors with lower ultra-violet light.
Biological control : Parasites and predators are released to attack their prey (scale pests) in interior plantscapes. Generally, several inoculative colonizations are required to establish the beneficial species on its host. Scale insects, such as hemispherical scale, that produce less honeydew are more accessible for biological control; whereas, heavy honeydew secreting scale, like brown soft scale, are less accessible to biological controls. Small plants can be tented or caged with fabric netting for release of predators and parasites to keep them near the target infestation. There can be "spill-over" onto alternate scale hosts when the favored host is not present, but this strategy requires higher numbers per release.
Commercial Predators that Eat Scale : Of the commercially available species, Lindorus lophanthae specializes on purple scale and many other armored scale pests with relatively thin scale covers and will feed on immature stages of soft scale. It is attracted to higher densities of scale. Cybocephalus sp. nr. nipponicus eats Euonymus scale. Green lacewing larvae feed on immature scales and some mature hard scales with thin covers. Cryptolaemus montrouzieri feeds on some scale species if mealybugs are not available. Sticky honeydew on soft scale is a deterrent to predators.

Releasing Lindorus with a fine paintbrush |
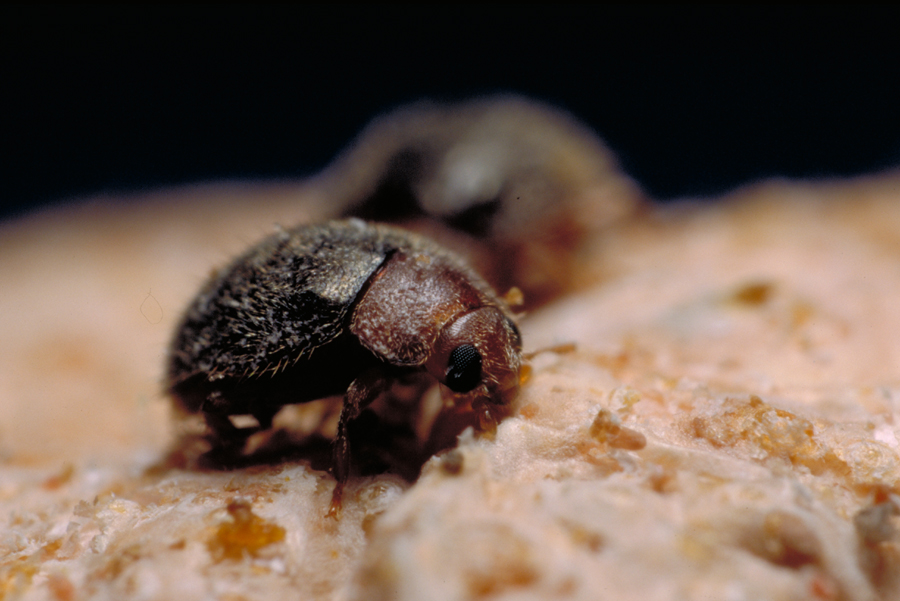

Lindorus lopanthae, general predator on armored scale |
Commercial Parasitoids that Attack Scale : One parasitoid Aphytis melinus is in commercial production. It attacks certain armored scale, but may not attack all species in a family, so get the scale identified. A. melinus adults host-feed, causing substantial mortality of scale stages not used for parasitism. requires immature scales approximately 0.5 to 1.5 mm in length ( that is, 2nd instar to early 3rd instar scales ) for egg laying. A. melinus parasitizes unmated 3rd instar female scale hosts. It is hindered by extreme cold, low humidity, and lack of susceptible host stage.
Regular releases in sufficient numbers can suppress or control infestations in two to three months. After this, 1-3 releases a year should be sufficient to maintain control. The number of parasitoids required for a release is completely dependent upon the number of scales present. A guideline rate is 5-10 parasitoids/infested plant or 10/square yard. Release 2-3 times at 2-3 week intervals. Reduce scale numbers, if possible, with insecticidal soap or soap and oil mixture 2-3 weeks before release. Remove ants and wash off honeydew accumulations just before release. M. helvolus is no longer commercially available.
Some Common Armored Scale Pests and Commercial Biocontrols
Toumeyella pini (Striped Pine Scale) Lindorus lophanthae and twice stabbed lady bird beetle are effective predators.
Chionaspis pinifoliae (Pine Needle Scale) Lindorus lophanthae and twice stabbed lady bird beetle are effective predators.
Aulacaspis yasumatsui (Cycad Aulacaspis Scale) Lindorus lophanthae and Cybocephalus binotatus are effective lady beetle predators.
Lepidosaphes beckii (Purple Scale). Citrus. Lindorus lophanthae is a lady beetle predator of purple scale normally present in California citrus.
Pulvinaria psidii (Green Shield Scale). On Ficus spp. and greenhouse ornamentals. M. helvolus will not parasitize it. Cryptolaemus montrouzieri will feed on this scale and help suppress it when mealybugs are not available.
Chrysomphalus aonidum (Florida Red Scale). On palms, banana. Lindorus lopanthae thrives on this armored scale. s will not attack it. Aphytis holoxanthus was being studied for control of this scale.
Some Common Soft Scale Pests and Commercial Biocontrols
Saissetia oleae (Black scale). On woody ornamentals. M. helvolus will parasitize it; however, it is no longer commercially available. Saissetia coffeae (Hemispherical scale). On ferns, Schefflera, and non-woody evergreens. M. helvolus has occasionally been reported to parasitize this scale (not commercially available.) Researchers at Texas A & M were looking at parasitoids (Metaphycus lounsburyi, etc.) for hemispherical scale which may be available in the future if the demand is great enough.
Saissetia nigra (Nigra scale). On citrus, hibiscus, and other tropical ornamentals. M. helvolus will parasitize it; however, it is no longer commercially available.
Saissetia miranda (Mexican black scale in greenhouses). On Ficus, Metaphycus helvolus will not parasitize. Search for a successful parasite is needed.
Coccus hesperidum (Brown soft scale). On Schefflera, weeping fig, ferns, and other ornamentals. Immatures can be confused with other soft scales. M. helvolus will not parasitize it. The parasitoids, Microterys flavus, and a newly imported Metaphycus spp. could some day be available.
Aspidiotus nerii (Ivy or oleander scale). Wide host range including palm and cycads. Lindorus lophanthae and Aphytis melinus control it.
Aonidiella aurantii (California red scale). Citrus, roses, and ornamentals. Lindorus lophanthae, green lacewing, and A. melinus work together to control it.
Diaspis boisduvallii (Boisduval's scale). Orchids, cacti, and sometimes palms. A. melinus does not establish on it. Lindorus lophanthae will feed and reproduce on it and Cryptolaemus montrouzier will feed on it and help suppress it when mealybugs are not available. Chrysomphalus dictyospermi (Dictyospermum scale). A. melinus parasitizes it, ideally used with Lindorus lopanthae.
Pinnaspis aspidistrae (Fern scale). Mondo grass; palms. A. melinus will not help. Effectiveness of predators is not known.
SCALE BIOCONTROLS Lindorus lopanthae and green lacewing favor soft scale if not too sticky. Cybocephalus is more specialized for certain scale. Cryptolaemus eat scale, but need mealybug to lay eggs. Aphytis melinus attacks certain armored scale, but may not attack all species in a family. Use of appropriate species in sufficient numbers in regular releases can suppress or control infestations in two to three months. Then, one to three releases per year should maintain control. Hot Pepper Wax sprays may help clean up some scale problems. |
|

|
| BENEFICIAL |
TARGET PEST |
RATE/FREQ |
CODE |
QUANTITY |
PRICE |
| Aphytis melinus
Golden Chalcidparasitic wasp
parsitizes 2nd, 3rd instar female, 2nd, pre pupal male, host feeds other stages
|
Armored scale, California red, citrus red, oleander, San Jose, ivy, walnut, Dytyospermum, and citrus yellow scale |
5K-10K/acre
1-2/ft2 GH
5-10/plant
1 wk I, 3 X |
AP5 |
5,000/cup |
18.00 |
| AP10 |
10,000/cup |
29.00 |
| 5+ cups |
24.00 |
| 10+ cups |
20.00 |
| AP30 |
30,000/cup |
68.00 |
| 5+ cups |
58.00 |
| 10+ cups |
54.50 |
Cybocephalus nipponicus
predatory beetle |
Euonymus scale, San Jose scale |
colony |
CYBO100 |
100/vial |
76.00 |
| 5+ vials |
69.00 |
| 10+ vials |
67.00 |
| Lindorus lopanthae
( also known as Rhyzobius lopanthae)
Scale Destroyerpredatory beetle
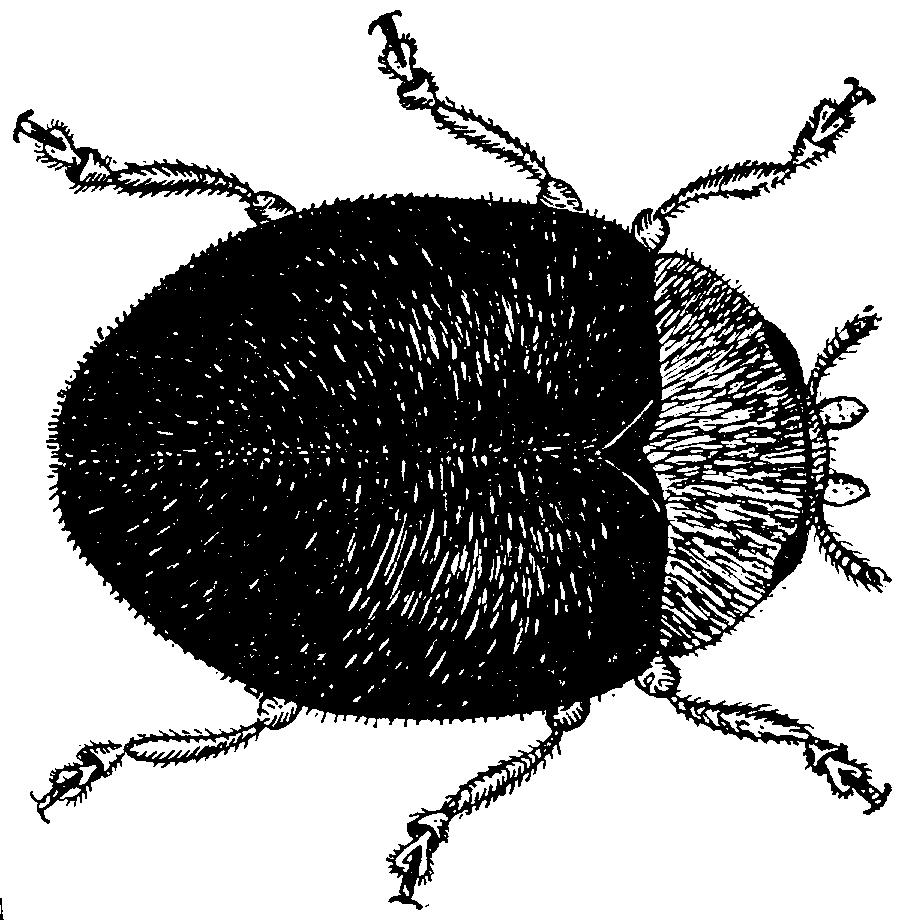
|
hard scale
soft scale until honey-dew forms, will eat some mealybug, other small insects,prefers 60-77° F, 20-90% RH
larvae, adult both predators
|
3-5/plant
20-40/tree1-2 K/acre3 wk I, 2 X
3-6/10 ft2 GH
|
LIN50 |
50/vial |
39.00 |
| 5+ vials |
25.00 |
| 10+ vials |
22.00 |
| LIN100 |
100/vial |
56.00 |
| 5+ vials |
43.00 |
| 10+ vials |
40.00 |
| LIN250 |
250/vial |
99.00 |
| 5+ vials |
88.00 |
| 10+ vials |
84.00 |
|

